REVIEW PAPER
Post-Mastectomy Breast Reconstruction – a review on current trends
1
Student Research Group at the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Medical University of Lublin, Poland
2
Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Medical University of Lublin, Poland
J Pre Clin Clin Res. 2024;18(1):33-39
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction and objective:
Mastectomy of the breast gland is a surgical procedure. It is one of the basic methods of treating breast cancer with stage I to III. Only in the case of stage IV cancer, it is not the basic method of treatment. Amputation of the breast gland is being used when the ongoing cancer process has affected more than one of the quarters of the breast. During this procedure, the wart and its areola are also removed, with the surrounding tissues (muscle fascia, lymph nodes, pectoral muscle). The aim of this study is to show different types of post-mastectomy breast reconstruction with their advantages and disadvantages
Review methods:
All relevant publications were retrieved from PubMed databases with the keywords including: “breast cancer”, “mastectomy”, “breast reconstruction”, “Post-mastectomy breast reconstruction”, “implant-based reconstruction”, “Fat Grafting reconstruction”, “Flaps based reconstruction”. The literature which was reviewed came from the last 10 years on methods of breast reconstruction after the mastectomy procedure.
Abbreviated description of the state of knowledge:
Statistics regarding breast cancer surgery procedures can vary based on factors such as geographic location, access to healthcare, advancements in medical technology, and individual patient preferences. However, some general trends and statistics regarding breast cancer surgery procedures include: BCS vs. Mastectomy: In recent years, lumpectomy (breast-conserving surgery) has become increasingly common, particularly for early-stage breast cancer. However, mastectomy rates vary depending on factors such as tumor size, tumor location, patient preference, and medical recommendations.
Summary:
Nowadays there are many methods including: implant-based reconstruction, fat grafting reconstruction, flapsbased reconstruction.
Mastectomy of the breast gland is a surgical procedure. It is one of the basic methods of treating breast cancer with stage I to III. Only in the case of stage IV cancer, it is not the basic method of treatment. Amputation of the breast gland is being used when the ongoing cancer process has affected more than one of the quarters of the breast. During this procedure, the wart and its areola are also removed, with the surrounding tissues (muscle fascia, lymph nodes, pectoral muscle). The aim of this study is to show different types of post-mastectomy breast reconstruction with their advantages and disadvantages
Review methods:
All relevant publications were retrieved from PubMed databases with the keywords including: “breast cancer”, “mastectomy”, “breast reconstruction”, “Post-mastectomy breast reconstruction”, “implant-based reconstruction”, “Fat Grafting reconstruction”, “Flaps based reconstruction”. The literature which was reviewed came from the last 10 years on methods of breast reconstruction after the mastectomy procedure.
Abbreviated description of the state of knowledge:
Statistics regarding breast cancer surgery procedures can vary based on factors such as geographic location, access to healthcare, advancements in medical technology, and individual patient preferences. However, some general trends and statistics regarding breast cancer surgery procedures include: BCS vs. Mastectomy: In recent years, lumpectomy (breast-conserving surgery) has become increasingly common, particularly for early-stage breast cancer. However, mastectomy rates vary depending on factors such as tumor size, tumor location, patient preference, and medical recommendations.
Summary:
Nowadays there are many methods including: implant-based reconstruction, fat grafting reconstruction, flapsbased reconstruction.
Garbacki K, Ciupak K, Bakalczuk P, Bakalczuk G. Post-Mastectomy Breast Reconstruction – a review on current trends. J Pre-Clin Clin Res. 2024; 18(1): 33–39. doi: 10.26444/jpccr/185444
REFERENCES (28)
1.
Filip CI, Jecan CR, Raducu L, Neagu TP, Florescu IP. Immediate Versus Delayed Breast Reconstruction for Postmastectomy Patients. Controversies and Solutions. Chirurgia (Bucur). 2017 Jul-Aug;112(4):378–386. doi:10.21614/chirurgia.112.4.378. PMID: 28862113.
2.
Chopra S, Al-Ishaq Z, Vidya R. The Journey of Prepectoral Breast Reconstruction through Time. World J Plast Surg. 2021 May;10(2):3–13. doi:10.29252/wjps.10.2.3. PMID: 34307092; PMCID: PMC8290458.
3.
Panchal H, Matros E. Current Trends in Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017 Nov;140(5S Advances in Breast Reconstruction):7S–13S. doi:10.1097/PRS.0000000000003941. PMID: 29064917; PMCID: PMC572222
4.
Peairs KS, Choi Y, Stewart RW, Sateia HF. Screening for breast cancer. Semin Oncol. 2017 Feb;44(1):60–72. doi:10.1053/j.seminoncol.2017.02.004. Epub 2017 Feb 13. PMID: 28395765.
5.
Kwong A, Shin VY, Ho JC, Kang E, Nakamura S, Teo SH, Lee AS, Sng JH, Ginsburg OM, Kurian AW, Weitzel JN, Siu MT, Law FB, Chan TL, Narod SA, Ford JM, Ma ES, Kim SW. Comprehensive spectrum of BRCA1 and BRCA2 deleterious mutations in breast cancer in Asian countries. J Med Genet. 2016 Jan;53(1):15–23. doi:10.1136/jmedgenet-2015-103132. Epub 2015 Jul 17. PMID: 26187060; PMCID: PMC4681590.
6.
Tosello G, Torloni MR, Mota BS, Neeman T, Riera R. Breast surgery for metastatic breast cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Mar 15;3(3):CD011276. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD011276.pub2. PMID: 29542106; PMCID: PMC6494198.
7.
Joo JH, Ki Y, Kim W, NamJ, KimD, ParkJ, KimHY, JungYJ, ChooKS, NamKJ, NamSB. Pattern of local recurrence after mastectomy and reconstruction in breast cancer patients: a systematic review. Gland Surg. 2021 Jun;10(6):2037–2046. doi:10.21037/gs-21–15. PMID: 34268088;PMCID: PMC8258883.
8.
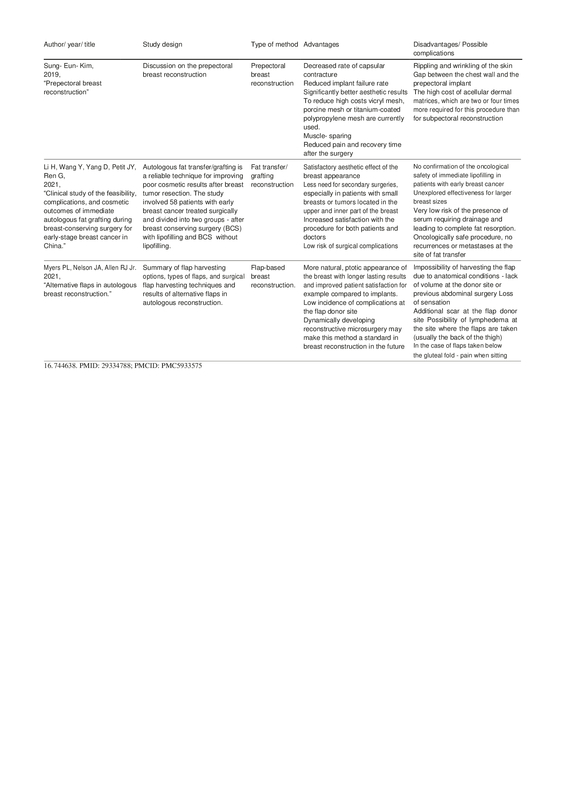
Kim SE. Prepectoral breast reconstruction. Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2019 Sep;36(3):201–207. doi:10.12701/yujm.2019.00283. Epub 2019 Aug 26. PMID: 31620634; PMCID: PMC6784648.
9.
Fairchild B, Ellsworth W, Selber JC, Bogue DP, Zavlin D, Nemir S, Checka CM, Clemens MW. Safety and Efficacy of Smooth Surface Tissue Expander Breast Reconstruction. Aesthet Surg J. 2020 Jan 1;40(1):53–62. doi:10.1093/asj/sjy199. PMID: 30107477; PMCID: PMC7317085.
10.
Walia GS, Aston J, Bello R, Mackert GA, Pedreira RA, Cho BH, Carl HM, Rada EM, Rosson GD, Sacks JM. Prepectoral Versus Subpectoral Tissue Expander Placement: A Clinical and Quality of Life Outcomes Study. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2018 Apr 20;6(4):e1731. doi:10.1097/GOX.0000000000001731. PMID: 29876176; PMCID:PMC5977939.
11.
Relations ASoPSP. 2016 Plastic Surgery Stastics Report: ASPS National Clearinghouse of Plastic Surgery Procedural Statistics. 2017.
12.
Li H, Wang Y, Yang D, Petit JY, Ren G. Clinical study of the feasibility, complications, and cosmetic outcomes of immediate autologous fat grafting during breast-conserving surgery for early-stage breast cancer in China. Gland Surg. 2021 Aug;10(8):2386–2397. doi:10.21037/gs-21-126. PMID: 34527550; PMCID: PMC8411079.
13.
Goncalves R, Mota BS, Sobreira-Lima B. et al. The oncological safety of autologous fat grafting: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer. 2022;22:391.
14.
Howes BH, Fosh B, Watson DI, Yip JM, Eaton M, Smallman A, Dean NR. Autologous fat grafting for whole breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2014 Apr 7;2(3):e124. doi:10.1097/GOX.0000000000000075. PMID: 25289318; PMCID:PMC4174150.
15.
Bellini E, Pesce M, Santi P, Raposio E. Two-Stage Tissue-Expander Breast Reconstruction: A Focus on the Surgical Technique. Biomed Res Int.2017;2017:1791546. doi:10.1155/2017/1791546. Epub 2017 Dec 10. PMID: 29376067; PMCID: PMC5742435.
16.
Turner A, Abu-Ghname A, Davis MJ, Winocour SJ, Hanson SE, Chu CK. Fat Grafting in Breast Reconstruction. Semin Plast Surg. 2020 Feb;34(1):17–23. doi:10.1055/s- 0039-1700959. Epub 2020 Feb 15. PMID: 32071575; PMCID: PMC7023975.
17.
Myers PL, Nelson JA, Allen RJ Jr. Alternative flaps in autologous breast reconstruction. Gland Surg. 2021 Jan;10(1):444–459. doi:10.21037/gs.2020.03.16. PMID: 33634002;PMCID: PMC7882326.
18.
Garza R 3rd, Ochoa O, Chrysopoulo M. Post-mastectomy Breast Reconstruction with Autologous Tissue: Current Methods and Techniques. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open.2021 Feb 18;9(2):e3433. doi:10.1097/GOX.0000000000003433. PMID: 33680677; PMCID: PMC7929567.
19.
Kaidar-Person O, Offersen BV, Boersma LJ, de Ruysscher D, Tramm T, Kühn T, Gentilini O, Mátrai Z, Poortmans P. A multidisciplinary view of mastectomy and breast reconstruction: Understanding the challenges. Breast. 2021 Apr;56:42–52. doi:10.1016/j.breast.2021.02.004. Epub 2021 Feb 10. PMID: 33610903; PMCID:PMC7905468.
20.
Chopra S, Al-Ishaq Z, Vidya R. The Journey of Prepectoral Breast Reconstruction through Time. World J Plast Surg. 2021 May;10(2):3–13. doi:10.29252/wjps.10.2.3. PMID: 34307092;PMCID: PMC8290458.
21.
Filip CI, Jecan CR, Raducu L, Neagu TP, Florescu IP. Immediate Versus Delayed Breast Reconstruction for Postmastectomy Patients. Controversies and Solutions. Chirurgia (Bucur). 2017 Jul-Aug;112(4):378–387. doi:10.21614/chirurgia.112.4.378. PMID: 28862113.
22.
Razdan SN, Patel V, Jewell S, McCarthy CM. Quality of life among patients after bilateral prophylactic mastectomy: a systematic review of patient-reported outcomes. Qual Life Res.2016 Jun;25(6):1409–21. doi:10.1007/s11136-015-1181-6. Epub 2015 Nov 14. PMID:26577764; PMCID: PMC4867133.
23.
Rini IS, Gunardi AJ, Yashinta, Kevin J, Marsaulina RP, Aryandono T, Dachlan I, Dwiprahasto I. Quality of Life in Palliative Post mastectomy Reconstruction: Keystone versus Rotational Flap. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2021 Mar 15;9(3):e3457. doi:10.1097/GOX.0000000000003457. PMID: 33747689; PMCID: PMC7963501.
24.
Champaneria MC, Wong WW, Hill ME, Gupta SC. The evolution of breast reconstruction: a historical perspective. World J Surg. 2012 Apr;36(4):730–42. doi:10.1007/s00268-012-1450-2. PMID: 22350474.
25.
McCrorie AD, Begley AM, Chen JJ, McCorry NK, Paget G, McIntosh SA. Improving preparedness prior to reconstructive breast surgery via inclusion of 3D images during pre-operative counselling: a qualitative analysis. BMC Womens Health. 2021 Aug 31;21(1):323. doi:10.1186/s12905-021-01463-6. PMID: 34465323; PMCID: PMC8408958.
26.
Evgeniou E, Teotia SS, Haddock NT. Asymmetric Four-Flap Breast Reconstruction with DIEP Flaps and PAP Flaps. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2022 Dec 1;150(6):1236e-1239e. doi:10.1097/PRS.0000000000009700. Epub 2022 Sep 15. PMID: 36103659.
27.
Goodenough CJ, Rose J. Breast Transverse Rectus Abdominus Muscle Procedure. 2023 May 29. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan–. PMID: 30969581.
28.
Sood R, Easow JM, Konopka G, Panthaki ZJ. Latissimus Dorsi Flap in Breast Reconstruction: Recent Innovations in the Workhorse Flap. Cancer Control. 2018 Jan-Mar;25(1):1073274817744638. doi: 10.1177/1073274817744638. PMID: 29334788; PMCID: PMC5933575.
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.