Editor's Choice
REVIEW PAPER
Efficacy of various forms of capsaicin in the treatment of neuropathic pain – literature review
1
Medical Department, Collegium Medicum, Jagiellonian University, Kraków, Poland
Corresponding author
Bartłomiej Cytlau
Medical Department, Jagiellonian University Collegium Medicum, św Anny 12, Kraków, Poland
Medical Department, Jagiellonian University Collegium Medicum, św Anny 12, Kraków, Poland
J Pre Clin Clin Res. 2024;18(4):312-316
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction and objective:
Pain is defined as a subjective, unpleasant sensation resulting from actual or potential tissue damage or nervous system malfunction. If left untreated or treated ineffectively, it leads to serious complications. Neuropathic pain is a particularly difficult type of pain to manage. The drugs used in its treatment include capsaicin (CP) – vanillyl amide, an antagonist of the transient receptor potential V1 (TRPV1) receptors, used for thousands of years in folk medicine and cooking.
Review methods:
The PubMed database was searched using the terms ‘capsaicin’, ‘pain”, and ‘neuropathic’, and the filters ‘Clinical Trial’ and ‘Randomized Controlled Trial’.A total of 94 articles were identified, 27 of which were eligible for review
Brief description of the state of knowledge:
Capsaicin, due to its unique mechanism of action, stands out from other analgesics. Its use in everyday clinical practice has been confirmed in many clinical studies. However, there are still medical disciplines in which its usage is unexplored and should be investigated. Moreover, when taking capsaicin, clinicians should also pay attention to possible side-effects
Summary:
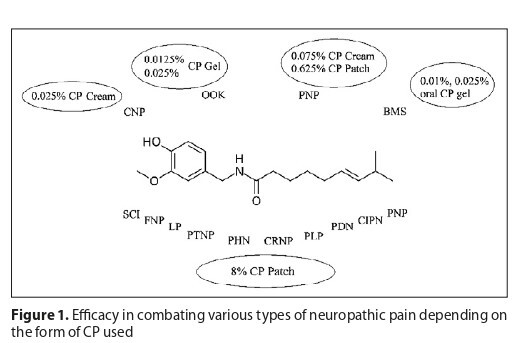
The discussed studies indicate the effectiveness of CP, used topically in the treatment of HIV-associated distal sensory polyneuropathy (HDSP), spinal cord injury, focal neuropathic pain, lumbosacral pain, post-traumatic neuropathic pain, cancer-related neuropathic pain, painful diabetic neuropathy (PDN), postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) and phantom limb pain. Characterized by a good safety profile, CP increasingly appears in the guidelines of scientific societies, and research on its use often goes beyond the issues described.
Pain is defined as a subjective, unpleasant sensation resulting from actual or potential tissue damage or nervous system malfunction. If left untreated or treated ineffectively, it leads to serious complications. Neuropathic pain is a particularly difficult type of pain to manage. The drugs used in its treatment include capsaicin (CP) – vanillyl amide, an antagonist of the transient receptor potential V1 (TRPV1) receptors, used for thousands of years in folk medicine and cooking.
Review methods:
The PubMed database was searched using the terms ‘capsaicin’, ‘pain”, and ‘neuropathic’, and the filters ‘Clinical Trial’ and ‘Randomized Controlled Trial’.A total of 94 articles were identified, 27 of which were eligible for review
Brief description of the state of knowledge:
Capsaicin, due to its unique mechanism of action, stands out from other analgesics. Its use in everyday clinical practice has been confirmed in many clinical studies. However, there are still medical disciplines in which its usage is unexplored and should be investigated. Moreover, when taking capsaicin, clinicians should also pay attention to possible side-effects
Summary:
The discussed studies indicate the effectiveness of CP, used topically in the treatment of HIV-associated distal sensory polyneuropathy (HDSP), spinal cord injury, focal neuropathic pain, lumbosacral pain, post-traumatic neuropathic pain, cancer-related neuropathic pain, painful diabetic neuropathy (PDN), postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) and phantom limb pain. Characterized by a good safety profile, CP increasingly appears in the guidelines of scientific societies, and research on its use often goes beyond the issues described.
Cytlau B, Łach A, Skorupa M, Marczyk Ł. Efficacy of various forms of capsaicin in the treatment of neuropathic pain based on literature review. J Pre-Clin Clin Res. 2024; 18(4): 312–316. doi: 10.26444/jpccr/193629
REFERENCES (44)
1.
Dydyk AM, Conermann T. Chronic Pain. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/b... (access: 2024.06.05).
2.
Ghlichloo I, Gerriets V. Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs). Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/b... (access: 2024.06.05).
3.
United Kingdom National Health Service. Side effects – Antidepressants 2021. https://www.nhs.uk/mental-heal... (access: 2024.06.05).
4.
Mutanana N, Tsvere M, Chiweshe MK. General side effects and challenges associated with anti-epilepsy medication: A review of related literature. Afr J Prim Health Care Fam Med. 2020 Jun 30;12(1):e1–e5. https://doi.org/10.4102/phcfm.....
5.
IASP. IASP Revises Its Definition of Pain for the First Time Since 1979. https://www.iasp-pain.org/wp-c... (access: 2024.06.05).
6.
Bouhassira D. Neuropathic pain: Definition, assessment and epidemiology. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2019 Jan-Feb;175(1–2):16–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neur....
7.
Finnerup NB, Attal N, Haroutounian S, et al. Pharmacotherapy for neuropathic pain in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2015 Feb;14(2):162–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-....
8.
Reyes-Escogido Mde L, Gonzalez-Mondragon EG, Vazquez-Tzompantzi E. Chemical and pharmacological aspects of capsaicin. Molecules. 2011 Jan 28;16(2):1253–1270. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecu....
9.
Adetunji TL, Olawale F, Olisah C, et al. Capsaicin: A Two-Decade Systematic Review of Global Research Output and Recent Advances Against Human Cancer. Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 13;12:908487. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2....
10.
Fattori V, Hohmann MS, Rossaneis AC, et al. Capsaicin: Current Understanding of Its Mechanisms and Therapy of Pain and Other Pre-Clinical and Clinical Uses. Molecules. 2016 Jun 28;21(7):844. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecu....
11.
Aghazadeh Tabrizi M, Baraldi PG, Baraldi S, et al. Medicinal Chemistry, Pharmacology, and Clinical Implications of TRPV1 Receptor Antagonists. Med Res Rev. 2017 Jul;37(4):936–983. https://doi.org/10.1002/med.21....
12.
Wang S, Bian C, Yang J, et al. Ablation of TRPV1+ Afferent Terminals by Capsaicin Mediates Long-Lasting Analgesia for Trigeminal Neuropathic Pain. eNeuro. 2020 May 29;7(3):ENEURO.0118-20.2020. https://doi.org/10.1523/ENEURO....
13.
Kilinc D, Gallo G, Barbee KA. Mechanical membrane injury induces axonal beading through localized activation of calpain. Exp Neurol. 2009 Oct;219(2):553–561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expn....
14.
Polydefkis M, Hauer P, Sheth S, et al. The time course of epidermal nerve fibre regeneration: studies in normal controls and in people with diabetes, with and without neuropathy. Brain. 2004 Jul;127(Pt 7):1606–15. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/....
15.
Abooj M, Bishnoi M, Bosgraaf CA, et al. Changes in spinal cord following inflammatory and neuropathic pain and the effectiveness of resiniferatoxin. The Open Pain Journal. 2016;9(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.2174/187638....
16.
Arora V, Campbell JN, Chung MK. Fight fire with fire: Neurobiology of capsaicin-induced analgesia for chronic pain. Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Apr;220:107743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phar....
17.
Stevens RM, Ervin J, Nezzer J, et al. Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Intraarticular Trans-Capsaicin for Pain Associated With Osteoarthritis of the Knee. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019 Sep;71(9):1524–1533. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.40....
18.
Billard M, Todhunter J, Fleming M, et al. A Phase 2 Double-Blind Clinical Trial to Examine the Comparative Effects on Osteoarthritic Knee Pain of CGS-200–1 (1% Capsaicin Topical Liquid), CGS-200–5 (5% Capsaicin Topical Liquid), and CGS-200–0 (Vehicle, No Capsaicin) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71.
19.
Campbell CM, Diamond E, Schmidt WK, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of injected capsaicin for pain in Morton’s neuroma. Pain. 2016 Jun;157(6):1297–1304. https://doi.org/10.1097/j.pain....
20.
Olusanya A, Yearsley A, Brown N, et al. Capsaicin 8% Patch for Spinal Cord Injury Focal Neuropathic Pain, a Randomized Controlled Trial. Pain Med. 2023 Jan 4;24(1): 71–78. https://doi.org/10.1093/pm/pna....
21.
Haanpää M, Cruccu G, Nurmikko TJ, et al. Capsaicin 8% patch versus oral pregabalin in patients with peripheral neuropathic pain. Eur J Pain. 2016 Feb;20(2):316–328. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejp.73....
22.
Zis P, Bernali N, Argira E, et al. Effectiveness and Impact of Capsaicin 8% Patch on Quality of Life in Patients with Lumbosacral Pain: An Open-label Study. Pain Physician. 2016 Sep-Oct;19(7):E1049–53.
23.
Mankowski C, Poole CD, Ernault E, et al. Effectiveness of the capsaicin 8% patch in the management of peripheral neuropathic pain in European clinical practice: the ASCEND study. BMC Neurol. 2017 Apr 21;17(1):80. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883....
24.
Musharraf MU, Ahmad Z, Yaqub Z. Comparison of topical capsaicin and topical turpentine Oil for treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2017 Jul-Sep;29(3):384–387.
25.
Irving G, Backonja M, Rauck R, et al. NGX-4010, a capsaicin 8% dermal patch, administered alone or in combination with systemic neuropathic pain medications, reduces pain in patients with postherpetic neuralgia. Clin J Pain. 2012 Feb;28(2):101–107. https://doi.org/10.1097/AJP.0b....
26.
Privitera R, Birch R, Sinisi M, et al. Capsaicin 8% patch treatment for amputation stump and phantom limb pain: a clinical and functional MRI study. J Pain Res. 2017 Jul 13;10:1623–1634. https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S1....
27.
Packham TL, Cappelleri JC, Sadosky A, et al. Measurement properties of painDETECT: Rasch analysis of responses from community-dwelling adults with neuropathic pain. BMC Neurol. 2017 Mar 4;17(1):48. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883....
28.
Raber JM, Reichelt D, Grüneberg-Oelker U, et al. Capsaicin 8 % as a cutaneous patch (Qutenza™): analgesic effect on patients with peripheral neuropathic pain. Acta Neurol Belg. 2015 Sep;115(3):335–343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760....
29.
Maihöfner CG, Heskamp ML. Treatment of peripheral neuropathic pain by topical capsaicin: Impact of pre-existing pain in the QUEPP-study. Eur J Pain. 2014 May;18(5):671–679. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1532....
30.
Sendel M, Dunst A, Forstenpointner J, et al. Capsaicin treatment in neuropathic pain: axon reflex vasodilatation after 4 weeks correlates with pain reduction. Pain. 2023 Mar 1;164(3):534–542. https://doi.org/10.1097/j.pain....
31.
Filipczak-Bryniarska I, Krzyzewski RM, Kucharz J, et al. High-dose 8% capsaicin patch in treatment of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: single-centre experience. Med Oncol. 2017 Aug 17;34(9):162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032....
32.
Kulkantrakorn K, Lorsuwansiri C, Meesawatsom P. 0.025% capsaicin gel for the treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy: a randomized, double-blind, crossover, placebo-controlled trial. Pain Pract. 2013 Jul;13(6):497–503. https://doi.org/10.1111/papr.1....
33.
Kulkantrakorn K, Chomjit A, Sithinamsuwan P, et al. 0.075% capsaicin lotion for the treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy: A randomized, double-blind, crossover, placebo-controlled trial. J Clin Neurosci. 2019 Apr;62:174–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn....
34.
McCleane G. Topical application of doxepin hydrochloride, capsaicin and a combination of both produces analgesia in chronic human neuropathic pain: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2000 Jun;49(6):574–579. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365....
35.
Persson MSM, Stocks J, Sarmanova A, et al. Individual responses to topical ibuprofen gel or capsaicin cream for painful knee osteoarthritis: a series of n-of-1 trials. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021 May 14;60(5):2231–2237. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheuma....
36.
Kosuwon W, Sirichatiwapee W, Wisanuyotin T, et al. Efficacy of symptomatic control of knee osteoarthritis with 0.0125% of capsaicin versus placebo. J Med Assoc Thai. 2010 Oct;93(10):1188–1195.
37.
Moon JY, Lee PB, Kim YC, et al. Efficacy and Safety of 0.625% and 1.25% Capsaicin Patch in Peripheral Neuropathic Pain: Multi-Centre, Randomized, and Semi-Double Blind Controlled Study. Pain Physician. 2017 Feb;20(2):27–35.
38.
Jørgensen MR, Pedersen AM. Analgesic effect of topical oral capsaicin gel in burning mouth syndrome. Acta Odontol Scand. 2017 Mar;75(2):130–136. https://doi.org/10.1080/000163....
39.
Blonde L, Umpierrez GE, Reddy SS, et al. American Association of Clinical Endocrinology Clinical Practice Guideline: Developing a Diabetes Mellitus Comprehensive Care Plan-2022 Update. Endocr Pract. 2022 Oct;28(10):923–1049. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epra....
40.
Pop-Busui R, Ang L, Boulton AJM, et al. Diagnosis and Treatment of Painful Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy. Arlington (VA): American Diabetes Association; 2022. https://doi.org/10.2337/db2022....
41.
Kolasinski SL, Neogi T, Hochberg MC, et al. 2019 American College of Rheumatology/Arthritis Foundation Guideline for the Management of Osteoarthritis of the Hand, Hip, and Knee. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 Feb;72(2):220–233. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.41....
42.
Araszkiewicz A, Bandurska-Stankiewicz E, Borys S, et al. 2022 Guidelines on the management of patients with diabetes. A position of Diabetes Poland. Current Topics in Diabetes. 2022;2(1):1–130. https://doi.org/10.5114/ctd/14....
43.
QUTENZA, R. G (capsaicin) topical system: US prescribing information https://www.qutenza.com/pdfs/Q... (access: 2024.06.05).
44.
Landrum O, Marcondes L, Egharevba T, et al. Painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy of the feet: integrating prescription-strength capsaicin into office procedures. Pain Manag. 2023 Oct;13(10):613–626. https://doi.org/10.2217/pmt-20....
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.